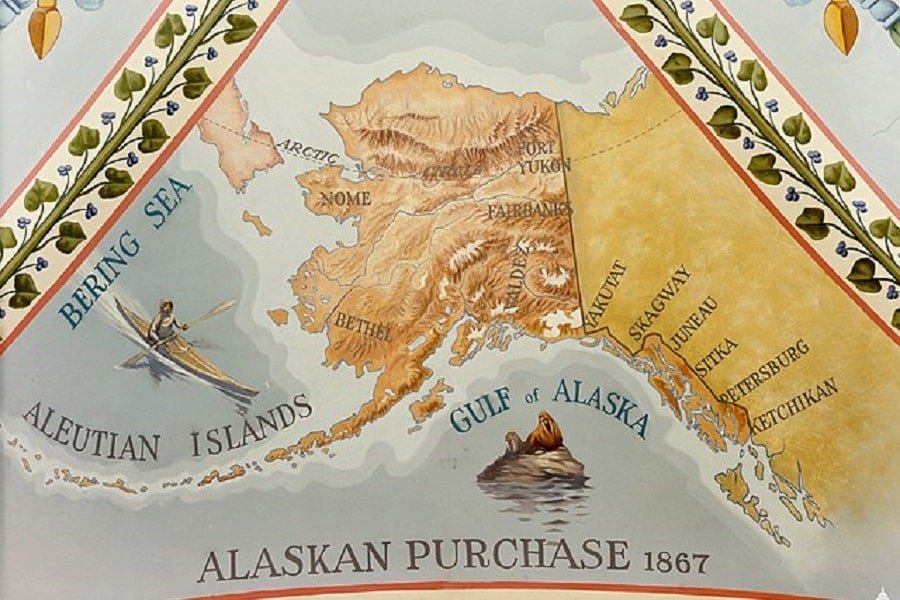
What is the biggest state in the United States (US)? With a total of 50 states, there is plenty to pick from. Off the top of one’s head, one might say Texas, or maybe California. However, the actual biggest state is one that doesn’t border any of the other states. Indeed, it’s the 49th state by the name of Alaska. By a landslide since it’s about twice the size of the second-biggest state.
Alaska is an absolute treasure for anyone remotely charmed by nature. With vast landscapes, plenty of wildlife, ample natural resources, and great sunsets, Alaska’s got it all. While natural beauty is under attack due to climate change, it remains the biggest state in US history.
But Alaska hasn’t always been part of the US. Only after the treaty, now known as Seward’s Folly, was Alaska integrated into US territory. Why is that the case, and what were the challenges and discussions surrounding Seward’s Folly treaty?
Table of Contents
The Backstory of Seward’s Folly
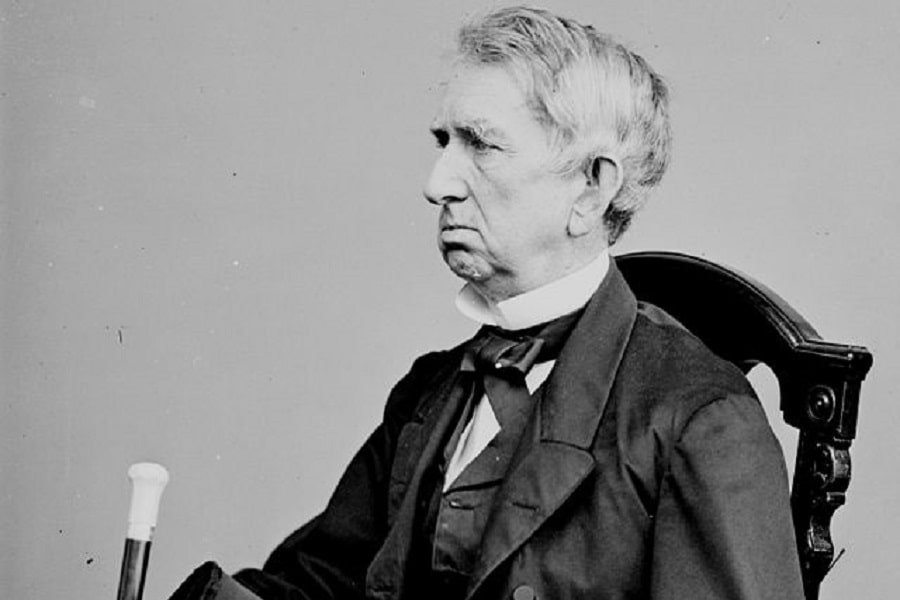
It is the early morning of March 30, the year 1867. A secretary of state, William H. Seward, was negotiating with Russian Minister Edouard de Stoeckl about a vast area that bordered the West of Canada. However, the area also shared a border with the most Eastern part of Russia.
What does the American secretary of state, William Seward, want to do with an area that doesn’t even border the country he represents?

Russia’s Presence in Alaska
To answer that question, we must go back to the first establishment of Russia. The first Russian explorer who tried to plant the Russian flag in Alaska’s land is Vitus Jonassen Bering. Indeed, the Bering Strait between Alaska and Asia would later be named after him.
After Russia established some explorers and citizens in the early 18th century, Russia approached the US about selling the territory. Unfortunately, the continuous American Civil War would stall the negotiations for quite some time.
President Andrew Johnson, an American Statesman, and a Russian Minister
Eventually, the civil war was somewhat resolved, and after a while , Andrew Johnson was in charge of the nation. President Andrew Johnson was supported by his secretary of state – William Seward. Discussing the territory where Russia established its latest explorers, they started to think about the purchase of Alaska. More specifically, they were charmed by all the natural resources on the Alaskan territory.
The offer from Russia was still on the table. They were very eager to sell the land. Why did Russia want the US to buy Alaska?
This is mostly because Alaska is a very remote area, quite hard to reach from the Russian mainland, and because it was prone to become a problem in the future. Rather than losing it in a battle with Great Britain, Russia thought it would be better to make some money off it. Since Russia was expanding in Asia anyway, they didn’t necessarily need the Alaskan territory.
Why did Russia sell Alaska to the US instead of Canada?
The Russians actively searched for someone other than Great Britain or Canada for the purchase of Alaska. Their opposition towards Great Britain was rooted in misplaced trust and several wars. The main reason that Russia didn’t want to sell Alaska to Canada was the Crimean war.
Indeed, the Crimean war was already a topic back in the 1850s and sadly continues to be an area of war well into the 21st century. The US, at the time, was too busy with its own civil unrest, meaning it didn’t mingle with the whole war in Europe. Because of this, the US had a favorable position in the eyes of the Russians for the purchase of Alaska.
So negotiations about the area that would significantly extend the Pacific coast of the US were picked up again. Seward and de Edouard de Stoeckl agreed on the purchase of Alaska for 7.2 million dollars. Converted to the equivalent for 2021, this would be around 140 million dollars.
The Treaty and Native Tribes
But what did Seward agree to?
The exact treaty outlines the geographical boundaries of the territory and establishes ownership of existing property. Of course, Russian citizens still lived in the area. They got the option to return to their home country within three years. If not, they would officially become US citizens.
However, the land was inhabited long before the treaty, which would become known as Seward’s Folly. Indeed, Native tribes were already living there for a long time. Still, this didn’t seem to matter one bit to the Americans or the Russians. The American government subjected them to the laws and regulations of the US government but fully rejected their eligibility for citizenship. Because of this, natives were often exploited or used as slaves.
Senate Vote and Seward’s Folly
Although the rejection of human rights made the purchase quite troublesome, Seward thought he did quite a good job. However, there had to be a majority in the Senate to complete the Alaska purchase.
At first, this was quite the problem, and the senate needed some conviction. Thanks to the support of senator Charles Sumner, the Senate approved the Alaska treaty by a vote of 37 to 2 on April 9th.

Critique of Seward’s Folly
However, acceptance by the Senate didn’t mean that everybody agreed with the purchase. Many were critical of the secrecy surrounding the deal. The purchase became known under its critics as ‘Seward’s Folly,’ ‘Seward’s icebox,’ and Johnson’s ‘polar bear garden.’
Seward’s Folly became quite a popular topic, and it would take another year before the actual purchase was finished. That is to say, the appropriation of money needed to purchase Alaska was delayed by more than a year due to opposition in the House of Representatives. The House finally approved the appropriation on July 14, 1868, by a vote of 113 to 43.
Why Was it Called Seward’s Folly?
Many people in the US government thought the land Seward was buying was not worth the price the nation was paying. It may have been approved, but the decision to purchse the Alaskan Territory did not escape ridicule.
Labelling it “Seward’s Folly” which is another way of saying “Seward’s Mistake” helped those who opposed the position make their perspective tht the deal was a bad one clear to the public.
Why did the US buy Alaska?
While the reasons for Russia selling Alaska are quite clear, the reasons for the purchase of Alaska by the US are still somewhat vague. To learn more about why the US bought Alaska, we should talk about its marine life.
America’s Motivation to Buy Alaska
Indeed, the Pacific coast of Alaska was one of the main reasons why the US wanted to purchase the region. In the 1860s, Alaska was famous for its long Pacific coast and, therefore, its abundance of seals and sea otters. Valuable sources, indeed, since their furs would generate a welcome income stream for US citizens and the whole economy.
While the fur trade was a big reason for the Alaska treaty and, eventually, the purchase of Alaska, there was another reason. A more strategic one, if you will. At the time, the region that we know today as Canada was ruled by the Brits. The US wanted to proceed with the Alaska purchase to inhibit Great Britain from expanding its overseas territory.
Why Did Seward Want Alaska?
Seward personally saw the purchase of Alaska as a great opportunity to simply expand. Seward was well aware of the geopolitical games that were being played on the other side of the ocean. As a relatively new country, the US grabbed any opportunity to expand with both hands to look more prestigious in the eyes of other world powers.
Alaska was, thus, mainly purchased because of its strategic importance.
What Happened After the Acquisition of Alaska
The ‘polar bear garden of Johnson’, or ‘Seward’s icebox’ was first seen as just an empty land. People did praise the bargain price for which it was bought but didn’t understand why the secretary of state bought it in the first place.
Gold Rush
While questioned in the beginning, just a couple of decades later, it became clear that the purchase might have been one of the most lucrative ones in American history.
It all started when gold was discovered in the Klondike in Canada’s Yukon territory. Thousands of prospectors rushed to the area to claim their gold fields. After a while, all was claimed, and people began searching for gold in Alaska. They discovered that the territory was filled with valuable goods, which made the area more attractive to gold diggers.
Still, only a few got lucky. But, it changed the population and spatial design of Alaska for good. Between 1897 and 1907, gold rushers founded more than fifty gold-mining camps in various parts of Alaska.
Over time, some of them grew into major towns with railroads, ports, and all that was necessary to live comfortably. Russians, too, settled in Alaska before and built their towns. However, because of the gold rush, most of the Russian heritage vanished, and the land became Americanized.
READ MORE: Who Invented the Railroad? Exploring the Fascinating History of Railroads

World War II and Japan
Although the new territory was bought as a geopolitical strategy, it was also quite vulnerable. Mainly because it was hard to defend. This was due to the fact that there was simply too much space to defend without any real border with the rest of the US. Japan was aware of this fact and started to exploit this opportunity during World War II.
The islands of Aguttu, Attu, and Kiska were taken in 1942. Although they were retaken quite easily by the US, the threat to Alaska prompted the construction of the Alcan Highway and increased its military presence.
Statehood
Right after the secretary of state William Seward accepted to purchase Alaska for
$7.2 million, the area was just used for its natural resources. Later it became more critical because of its gold, but it never really gained official statehood as part of the US.
The conversion of Alaska into an official state only took place right after World War II, in 1946. In 1955, a state constitution was officially adopted, and in 1959 president Eisenhower announced Alaska’s entrance into the Union as the 49th state. Just nine months later, Hawai’i was also granted statehood, bringing the total up to 50 states.